Types of dna Mutations

Types of CFTR Mutations Some genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, are caused by mutations in a single gene. A gene contains DNA “letters” that spell out the instructions to make a specific protein.
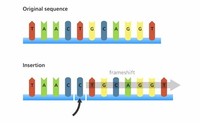
An insertion is when base pairs are added to a DNA sequence, and a deletion is when base pairs are removed from a DNA sequence. Learning Outcome After this lesson, you will be able to describe what happens during the two types of point mutations: base substitutions and insertions and deletions.

Sickle cell disease is a group of disorders that affects hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that delivers oxygen to cells throughout the body. People with this disorder have atypical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort red blood cells into a sickle, or crescent, shape.

Mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. Based on the effect of mutation on the gene structure, mutations may be: (1) small-scale mutations or (2) large scale mutations.

Mutations in the HEXA gene cause Tay-Sachs disease. The HEXA gene provides instructions for making part of an enzyme called beta-hexosaminidase A, which plays a critical role in the brain and spinal cord. This enzyme is located in lysosomes, which are structures in cells that break down toxic substances and act as recycling centers. Within lysosomes, beta-hexosaminidase A helps break down a fatty substance called GM2 ganglioside.