Types of Ectopic Pregnancy

In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg doesn’t attach to the uterus. Instead, it may attach to the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix. While a pregnancy test may reveal a woman is pregnant, a fertilized egg can’t properly grow anywhere other than the uterus.

A heterotopic pregnancy is a rare complication of pregnancy in which both extra-uterine (ectopic pregnancy) and intrauterine pregnancy occur simultaneously. It may also be referred to as a combined ectopic pregnancy, multiple‑sited pregnancy, or coincident pregnancy.

Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, Risks and Treatment An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg attaches itself in a place other than inside the uterus. Almost all ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube and are thus sometimes called tubal pregnancies.
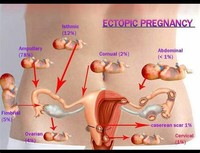
Ectopic pregnancy can lead to fallopian tube rupture. If that happens, you could have major pain and severe bleeding. Call your doctor immediately if you have heavy vaginal bleeding that causes lightheadedness, fainting, or shoulder pain.