Types of Enterobacteriaceae

The Enterobacteriaceae are a large family of Gram-negative bacteria.This family is the only representative in the order Enterobacteriales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria.

Buchnera aphidicola, a member of the Proteobacteria, is the primary endosymbiont of aphids, and has been studied in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Buchnera is believed to have had a free-living, Gram-negative ancestor similar to a modern Enterobacteriaceae, such as Escherichia coli.

Cedecea species 012 (also known as Cedecea species 5) Cedecea is a genus of extremely rare bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The name of this genus was derived from CDC, the abbreviation for the Centers for Disease Control where the initial members of this genus were discovered.

Citrobacter freundii is a species of facultative anaerobic gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The bacteria have a long rod shape with a typical length of 1–5 μm. Most C. freundii cells generally have several flagella used for locomotion, but some do not and are non-motile.

Citrobacter koseri is a Gram-negative, nonspore-forming bacillus. It is a facultative anaerobe capable of aerobic respiration. It is motile via peritrichous flagella. It is a member of the family of Enterobacteriaceae. The members of this family are the part of the normal flora of human and animal digestive tracts.

Cronobacter sakazakii (Farmer et al. 1980) Cronobacter sakazakii, which before 2007 was named Enterobacter sakazakii, is an opportunistic Gram-negative, rod-shaped, pathogenic bacterium that can live in very dry places.
Dickeya dadantii is a gram-negative bacillus that belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae.It was formerly known as Erwinia chrysanthemi but was reassigned as Dickeya dadantii in 2005.
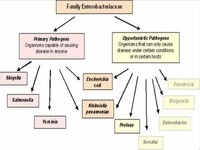
Enterobacteriaceae includes, along with many harmless symbionts, many of the more familiar pathogens, such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, Klebsiella, and Shigella. Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include Proteus, Enterobacter, Serratia, and Citrobacter.

Edwardsiella tarda is a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family. The bacterium is a facultatively anaerobic, small, motile, gram negative, straight rod with flagella.

A 2012 study in which Enterobacter cloacae transplanted into previously germ-free mice resulted in increased obesity when compared with germ-free mice fed an identical diet, suggesting a link between obesity and the presence of Enterobacter gut flora.

Erwinia is a genus of Enterobacteriaceae bacteria containing mostly plant pathogenic species which was named for the famous plant pathologist, Erwin Frink Smith. It contains Gram-negative bacteria related to Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, and Yersinia. They are primarily rod-shaped bacteria. Many infect woody plants.

Pantoea agglomerans is a Gram-negative bacterium that belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Formerly called Enterobacter agglomerans or Erwinia herbicola, it is an ubiquitous bacterium commonly isolated from plant surfaces, seeds, fruit, and animal or human feces. P. agglomerans can be found throughout a honeybee's environment.

The Enterobacteriaceae are a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. This family is the only representative in the order Enterobacteriales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria.

Hafnia psychrotolerans Hafnia is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae. H. alvei is a commensal of the human gastrointestinal tract and not normally pathogenic, but may cause disease in immunocompromised patients.

Enterobacteriaceae includes, along with many harmless symbionts, many of the more familiar pathogens, such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, Klebsiella, and Shigella. Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include Proteus, Enterobacter, Serratia, and Citrobacter.

Enterobacteriaceae includes, along with many harmless symbionts, many of the more familiar pathogens, such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, Klebsiella, and Shigella. Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include Proteus, Enterobacter, Serratia, and Citrobacter.

Kluyvera ascorbata is a bacterium, the type species of its genus. It is Gram-negative, rod-shaped and motile with peritrichous flagella.. References

Luttrell, R. E.; et al. (1988). "Kluyvera species soft tissue infection: case report and review". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 26 (12): 2650–2651. GIL D DE, M. O. N. I. C. A., et al. "Bacteremia por Kluyvera cryocrescens: Reporte de dos casos clínicos." Revista chilena de infectología 18.1 (2001): 72-74.

M. morganii is a member of the tribe Proteeae (normal fecal flora that often causes infection in patients whose normal flora have been disturbed by antibiotic therapy) of the family Enterobacteriaceae, with two species: M. morganii and M. sibonii.

Pectobacterium carotovorum is a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae; it used to be a member of the genus Erwinia. The species is a plant pathogen with a diverse host range, including many agriculturally and scientifically important plant species. It produces pectolytic enzymes that hydrolyze pectin between individual plant cells.

Photorhabdus luminescens (previously called Xenorhabdus luminescens) is a Gammaproteobacterium, belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, and is a lethal pathogen of insects. It lives in the gut of an entomopathogenic nematode of the family Heterorhabditidae.

Plesiomonas shigelloides is a species of bacteria that was formerly classified in the family Vibrionaceae, but now most microbiologists agree that a better classification is in the family Enterobacteriaceae (see box on the right).

Proteus mirabilis appears as Gram-negative rods after Gram staining under bright-field microscopy with 1000 times magnification. Proteus mirabilis is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium.

Enterobacteriaceae (of which Proteus is a member) and Pseudomonas species are the micro-organisms most commonly responsible for Gram-negative bacteremia and sepsis. The presence of the sepsis syndrome associated with a urinary tract infection (UTI) should raise the possibility of urinary tract obstruction.

Providencia rettgeri (commonly P. rettgeri), is a Gram negative bacterium that is commonly found in both water and land environments. P. rettgeri is in the genus Providencia, along with Providencia stuartii, Providencia alcalifaciens, and Providencia rustigianii. P. rettgeri can be incubated at 37 °C in nutrient agar or nutrient broth.
Providencia stuartii (commonly P. stuartii), is a Gram negative bacterium that is commonly found in soil, water, and sewage. P. stuartii is the most common of the 5 species found in the genus Providencia, with Providencia rettgeri, Providencia alcalifaciens, Providencia rustigianii, P heimbachae.

Raoultella planticola is a Gram-negative bacterium of the genus Raoultella. R. planticola is quite similar in appearance to Klebsiella pneumoniae and must be identified based on growth habits or DNA analysis.
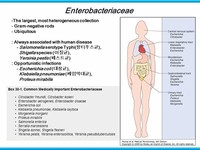
The Enterobacteriaceae are a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. This family is the only representative in the order Enterobacteriales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria.

Serratia marcescens Bizio 1823 Serratia marcescens (/ s ə ˈ r eɪ ʃ i ə m ɑːr ˈ s ɛ s ɪ n z /) is a species of rod-shaped gram-negative bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae.

Enterobacteriaceae includes, along with many harmless symbionts, many of the more familiar pathogens, such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, Klebsiella, and Shigella. Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include Proteus, Enterobacter, Serratia, and Citrobacter.

Enterobacteriaceae includes, along with many harmless symbionts, many of the more familiar pathogens, such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, Klebsiella, and Shigella. Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include Proteus, Enterobacter, Serratia, and Citrobacter.

Yersinia, (genus Yersinia), any of a group of ovoid- or rod-shaped bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Yersinia are gram-negative bacteria and are described as facultative anaerobes, which means that they are capable of surviving in both aerobic and anaerobic environments.