Types of Female Cancer
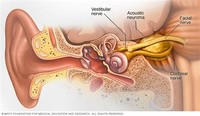
Acoustic Neuroma Causes There are two types of acoustic neuroma: a sporadic form and a form associated with a syndrome called neurofibromatosis type II (NF2). NF2 is an inherited disorder characterized by the growth of noncancerous tumors in the nervous system.

Astrocytoma is the most common a type of glioma tumor that can develop in the brain and spinal cord. It’s more common in men than women and most often shows up after age 45. There are several types of astrocytoma, and some grow faster than others.

Based on current incidence rates, 12.4 percent of women born in the United States today will develop breast cancer at some time during their lives . This estimate, from the most recent SEER Cancer Statistics Review (a report published annually by the National Cancer Institute’s [NCI] Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results [SEER] Program), is based on breast cancer statistics for the years 2007 through 2009.

Cervical cancer starts in the cells lining the cervix -- the lower part of the uterus (womb). This is sometimes called the uterine cervix. The fetus grows in the body of the uterus (the upper part). The cervix connects the body of the uterus to the vagina (birth canal).

Chordoma is a kind of cancer that grows in the bones of your skull and spine. It's very rare. Only 1 out of every 1 million people gets it. About 300 people are diagnosed with chordoma in the United States each year. You can get it at any age -- even in childhood. But most people are diagnosed between ages 40 and 70. Men get it more often than women.
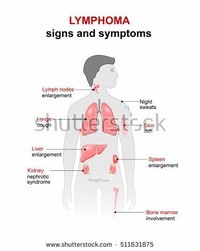
Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lymph tissue of the brain and/or spinal cord. Lymphoma is a disease in which malignant cells form in the lymph system.

Colon and rectal cancer:268,783 lives Colon cancer grows in the tissues of the colon, whereas rectal cancer grows in the last few inches of the large intestine near ...

Craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor that mostly affects children between the ages of 5 and 14. Adults sometimes get them, too. They grow near the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. Craniopharyngiomas are made up of solid parts and fluid-filled pockets called cysts.

Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a group of rare tumors that involve abnormal growth of cells inside a woman's uterus. GTD does not develop from cells of the uterus like cervical cancer or endometrial (uterine lining) cancer do.

But when you have leukemia, your body makes more white cells than it needs. There are two main types of white blood cells in your body: lymphoid cells and myeloid cells. Leukemia can happen in either type. These leukemia cells can’t fight infection the way normal white blood cells do.

Liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in the United States. The number of deaths was 6.4 per 100,000 men and women per year based on 2011-2015 deaths. The number of deaths was 6.4 per 100,000 men and women per year based on 2011-2015 deaths.

Lung and bronchial cancer: 792,495 lives Lung and bronchial cancer is the top killer cancer in the United States. Smoking and use of tobacco products are the major causes of it, and it strikes most often between the ages of 55 and 65, according to the NCI. There are two major types: non-small cell lung cancer, which is the most common, and small cell lung cancer, which spreads more quickly. More than 157,000 people are expected to die of lung and bronchial cancer in 2010.

Gender: Medulloblastoma is more common in boys than girls. In adults, it is also more common in men than in women. Genetic conditions: People with cancer predisposition syndromes like Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Turcot syndrome and Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome) are more likely to develop medulloblastoma.

A meningioma is a tumor that forms on membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord just inside the skull. Specifically, the tumor forms on the three layers of membranes that are called meninges. These tumors are often slow-growing.

Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (also known as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, NHL, or sometimes just lymphoma) is a cancer that starts in white blood cells called lymphocytes, which are part of the body’s immune system.

About 33 percent of all brain tumors are gliomas, which originate in the glial cells that surround and support neurons in the brain, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells. Gliomas are called intra-axial brain tumors because they grow within the substance of the brain and often mix with normal brain tissue.

Women with PPC usually get the same treatment as those with widespread ovarian cancer. This could include surgery to remove as much of the cancer as possible (a process called debulking that is discussed in the section about surgery), followed by chemotherapy like that given for ovarian cancer.

A pancreatic cancer prognosis depends a great deal on the cancer’s stage at the time of diagnosis. Advanced stages of pancreatic cancer are generally more fatal than early stages, due to the spread of the disease.

Primary peritoneal cancer is more common in women than in men. Women at risk for ovarian cancer are also at increased risk for peritoneal cancer. This is even more likely if you have the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic mutations.

Prostate cancer: 144,926 lives This cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths in men, after lung and bronchial cancer, according to the NCI. Prostate cancer usually starts to grow slowly in the prostate gland, which produces the seminal fluid to transport sperm.

Uterine (endometrial) cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women in the U.S. Read about uterine cancer symptoms, signs, prognosis, survival rate, treatment and more. Discover what causes uterine cancer, types of uterine cancer, and the difference between stages 1, 2, 3, and 4.

Women who haven’t been exposed to it can still get vaginal cancer, but the chances are very small. If DES isn’t a factor, clear cell carcinoma is most likely to happen after menopause. Vaginal Cancer and HPV. About nine out of every 10 vaginal cancer cases are linked to human papilloma virus, or HPV, infection. This is the most common STI, or sexually transmitted infection.

What Is Vulvar Cancer? The vulva is the outer part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the opening of the vagina (sometimes called the vestibule), the labia majora (outer lips), the labia minora (inner lips), and the clitoris.