Types of Gasifiers

Types of Gasifiers Updraught or counter current gasifier The oldest and simplest type of gasifier is the counter current or up-draught gasifier shown

2.3.3. Cross-draught gasifier. Cross-draught gasifiers, schematically illustrated in Figure 2.9 are an adaptation for the use of charcoal. Charcoal gasification results in very high temperatures (1500 °C and higher) in the oxidation zone which can lead to material problems. In cross draught gasifiers insulation against these high temperatures is provided by the fuel (charcoal) itself.

Fluidized-bed gasifiers suspend feedstock particles in an oxygen-rich gas so the resulting bed within the gasifier acts as a fluid. These gasifiers employ back-mixing, and efficiently mix feed coal particles with coal particles already undergoing gasification.

2.3.5 Other types of gasifiers 2.3.1 Updraught or counter current gasifier The oldest and simplest type of gasifier is the counter current or updraught gasifier shown schematically in Fig. 2.7.
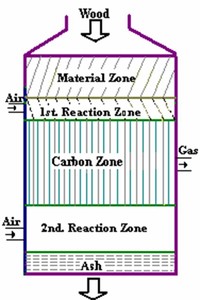
2.3.2 Downdraught or co-current gasifiers A solution to the problem of tar entrainment in the gas stream has been found by designing co-current or downdraught gasifiers, in which primary gasification air is introduced at or above the oxidation zone in the gasifier.