Types of Gastrointestinal Disorders

People with functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorders can have a variety of symptoms that range from painless diarrhea or constipation, to pain associated with diarrhea and/or constipation (usually called irritable bowel syndrome).

Many variations of appendicitis symptoms and signs occur. Pain may not be localized, particularly in infants and children. Tenderness may be diffuse or, in rare instances, absent. Bowel movements are usually less frequent or absent; if diarrhea is a sign, a retrocecal appendix should be suspected. RBCs or WBCs may be present in the urine. Atypical symptoms are common among elderly patients and pregnant women; in particular, pain is less severe and local tenderness is less marked.

Belching or passing gas (flatus) is natural and common. Excessive belching or flatus, accompanied by bloating, pain or distention, can occasionally interfere with daily activities or cause embarrassment. But these signs and symptoms usually don't represent any serious underlying condition and are often decreased with simple lifestyle measures.

Celiac disease tends to run in families, as it is a genetic disorder. If you have a parent, child, brother, or sister who has celiac disease, you have a 1 in 10 chance of getting it yourself. But having the genes for celiac disease doesn't automatically mean you'll get it.

So, cholera is caused by the Vibrio cholerae bacteria, and is the most common cause of bacterial gastroenteritis in the developing world. A lot of the symptoms of cholera overlap with the symptoms of the other forms of gastroenteritis, like vomiting and nausea and abdominal pain.

Crohn's disease is treated primarily with medications, including: Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as salicylates. Examples include mesalamine (Asacol, Lialda, Pentasa), olsalazine (Dipentum), and sulfasalazine (Azulfidine). Side effects include gastrointestinal upset, headache, nausea, diarrhea, or rash.

However, because other disorders (eg, appendicitis, colon or ovarian cancer, IBD) may cause similar symptoms, testing is required. Diverticulitis is evaluated with CT of the abdomen and pelvis with water-soluble contrast given orally and rectally; IV contrast also is given when not contraindicated. However, findings in about 10% of patients ...

Dysentery is an inflammation of the intestines, especially the colon. Symptoms include stomach cramps and diarrhea with blood or mucus in the feces. Many people have mild symptoms, but dysentery can be fatal if a person becomes dehydrated. Caused by an infection, some people may require antibiotics to help clear it up.

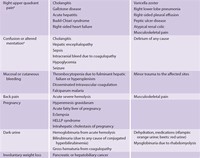
It may be described as indigestion, gassiness, early satiety, postprandial fullness, gnawing, or burning. Etiology There are several common causes of dyspepsia (see Table: Some Causes of Dyspepsia).


Findings suggestive of gastroenteritis include copious, watery diarrhea; ingestion of potentially contaminated food (particularly during a known outbreak), untreated surface water, or a known GI irritant; recent travel; or contact with certain animals or similarly ill people.

Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach. Many people, including pregnant women, suffer from heartburn or acid indigestion caused by GERD.

Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach. Many people, including pregnant women, suffer from heartburn or acid indigestion caused by GERD.
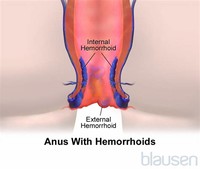
A hemorrhoid outside the anus that has a blood clot in it is called a thrombosed external hemorrhoid. Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids can usually be diagnosed with a rectal and anal examination. The doctor will examine the anus and rectum to look for swollen blood vessels that indicate there are hemorrhoids.

But for people with IBS, daily life is greatly influenced by the way their digestive system behaves. A flare-up of symptoms can mean hours of misery. "IBS is an illness which seems to strike people down," says Roberts, president of the IBS Self Help and Support Group.
Also, many disorders that cause jaundice cause other symptoms or serious problems. These symptoms may include nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, and small spiderlike blood vessels that are visible in the skin (spider angiomas).

Nausea and Vomiting - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the MSD Manuals - Medical Professional Version.

You can have ulcers at any age, but your chances go up as you get older. Causes. Ulcers form when digestive juices damage the walls of the stomach or small intestine. If the mucus layer gets too thin or your stomach makes too much acid, your gut will feel it. The two major causes are: Bacteria.

Ulcerative Colitis - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the MSD Manuals - Medical Professional Version.