Types of Genetic Screening

Lab tests can be done to check for the enzymes that are lacking in people that have Tay-Sachs disease. More cases can be found using lab tests than through DNA testing alone. Biochemical genetic studies may be done from a blood or urine sample, spinal fluid, or other tissue sample.
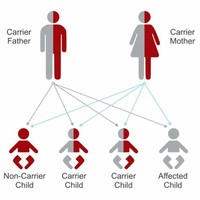
What is genetic carrier screening? Carrier screening is testing that's done to see whether you or your partner carry a genetic mutation that could cause a serious inherited disorder in your baby. Some of the more common disorders screened for include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, thalassemia, and Tay-Sachs disease, but there are more than 100 others that can be tested for.

Genetic testing can provide information about a person's genes and chromosomes. Available types of testing include: Newborn screening. Newborn screening is used just after birth to identify genetic disorders that can be treated early in life.

Diagnostic genetic testing can usually work out if you have a specific genetic condition that your provider is concerned about. It gives a “yes or no” answer. Your doctor may suggest a diagnostic genetic test if you have a medical problem.

Genetic testing is a type of medical test that identifies changes in chromosomes, genes, or proteins. The results of a genetic test can confirm or rule out a suspected genetic condition or help determine a person’s chance of developing or passing on a genetic disorder.

Newborn genetic screening is a health program that identifies treatable genetic disorders in newborn infants. Early intervention to treat these disorders can eliminate or reduce symptoms that might otherwise cause a lifetime of disability.

Preimplantation genetic diagnosis begins with the normal process of in vitro fertilization that includes egg retrieval and fertilization in a laboratory. Over the next three to five days, the embryos will divide into multiple cells.

Prenatal genetic screening tests of the pregnant woman’s blood and findings from ultrasound exams can screen the fetus for aneuploidy; defects of the brain and spine called neural tube defects; and some defects of the abdomen, heart, and facial features.