Types of Glands

Unlike adrenal fatigue, this is a recognized disease that can be diagnosed. There are two forms of this condition, and both are caused by damage or problems with your adrenal glands that result in them not making enough of the hormone cortisol.

Production, Function, Salts, Storage, Secretion What is Bile? Production, Function, Salts, Storage, ... Bile is a digestive juice that is secreted by the liver and ...

A: The gastric gland is the primary secretory unit of the stomach. The gastric gland is an essential body component because it secretes gastric juice and protective mucus. Mucus coats the stomach and helps it dilute enzymes and acids during the digestive process.
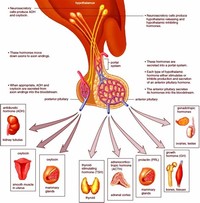
The hypothalamus is a small but crucial part of the brain. It controls several important functions, including sleep and growth. Learn more about its different parts and some of the conditions that affect it.

The hypothalamus is a small but crucial part of the brain. It controls several important functions, including sleep and growth. Learn more about its different parts and some of the conditions that affect it.

Functioning as an endocrine gland, the pancreas secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon to control blood sugar levels throughout the day. Both of these diverse functions are vital to the body’s survival.
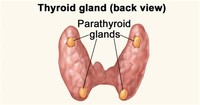
Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods that produce parathyroid hormone. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, variably located on the back of the thyroid gland.

The pineal gland, also known as the conarium or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles.

The pineal gland, also known as the conarium or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles.

The pineal gland, also known as the conarium or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles.

The pituitary gland is often called the master gland because it controls several other hormone glands in your body, including the thyroid and adrenals, the ovaries and testicles.

The pituitary gland may be smaller than usual. Primary ESS can be associated with obesity and high blood pressure in women. The function of the pituitary gland is usually normal and may be an incidental finding when a brain MRI scan is done for other reasons. Secondary ESS is the result of the pituitary gland regressing within the cavity after an injury, surgery or radiation therapy.

The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, letting urine flow out of the body.

The major glands of the endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pineal body, and the reproductive organs (ovaries and testes). The pancreas is also a part of this system; it has a role in hormone production as well as in digestion.

The _____ and _____ are the glands that stimulate reproductive cycles. was asked by Shelly Notetaker on May 31 2017. 1299 students have viewed the answer on StudySoup. View the answer on StudySoup.

sweat glands Tiny, coiled tubular glands deep in the skin that open either directly on to the surface or into hair follicles and secrete a salty liquid. Apocrine glands occur only on hairy areas and open into hair follicles. Apocrine sweat contains organic matter that can be decomposed by skin bacteria and cause odours.

The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts specifically to foreign invaders.
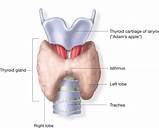
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland that sits low on the front of the neck. Your thyroid lies below your Adam’s apple, along the front of the windpipe. The thyroid has two side lobes, connected by a bridge (isthmus) in the middle.
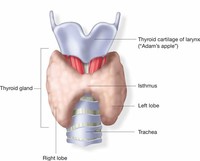
Overview of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped endocrine organ located at the base of your neck.This article explains how the thyroid gland works, including the symptoms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.