Types of Gynecologists

Adhesiolysis At the Vital Health we have successfully treated hundreds of patients with severe adhesions, and for some their surgery was not only life changing but life saving. Our adhesion patients are offered the same ongoing follow-up care as our endometriosis patients.
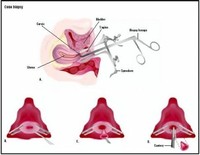
Cone biopsy is another, more invasive, way for your doctor to take a tissue sample, so it’s usually performed in a hospital. It can also treat some early-stage cervical cancers. Your doctor removes a cone-shaped piece of tissue from your cervix with either a LEEP, scalpel or laser.
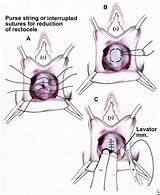
During the surgery, the bladder is pushed back into its normal position and the support tissue between the front of the vagina and the bladder is tightened and reinforced. The procedure is also called an anterior vaginal wall repair or anterior colporrhaphy.

A colposcopy is a simple 10- to 15-minute procedure that is painless and performed in a gynecologist's office. In fact, you can expect your colposcopy appointment to be similar to your Pap smear appointment.

Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a brief surgical procedure in which the cervix is dilated and a special instrument is used to scrape the uterine lining. Knowing what to expect before, during, and after a D&C may help ease your worries and make the process go more smoothly.

Endometrial ablation is a gynecological procedure that destroys the lining of the uterus in order to decrease the amount of bleeding during menstruation. Different methods are available, including the use of heat, cold, microwave energy, or high-evergy radio frequencies.

An endometrial biopsy is usually done by a gynecologist, a family medicine physician, or a nurse practitioner who has been trained to do the test. The sample will be looked at by a pathologist. The biopsy can be done in your doctor's office.

Ultrasound is an instrument that utilizes sound waves to visualize various internal structures and operates on the same principle as sonar on a submarine. In gynecology, ultrasound is used to evaluate conditions such as abnormal bleeding, uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts.