Types of History

The Early Cretaceous/Middle Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 146 Ma to 100 Ma.

The Eocene ( / ˈ iː ə ˌ s iː n, ˈ iː oʊ-/) Epoch, lasting from , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch.

The Jurassic period is divided into three epochs: Early, Middle, and Late. Similarly, in stratigraphy, the Jurassic is divided into the Lower Jurassic, Middle Jurassic, and Upper Jurassic series of rock formations.

The Late Triassic is the third and final of three epochs of the Triassic Period in the geologic timescale.The Triassic-Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth.

The Mesozoic Era began 252 million years ago with the largest mass extinction in Earth's history and ended 66 million years ago with the asteroid...

The Messinian Salinity Crisis ended with the Strait of Gibraltar finally reopening 5.33 Ma, when the Atlantic rapidly filled up the Mediterranean basin in what is known as the Zanclean flood.

The Mississippian Period began about 1,000 years ago. It's called "Mississippian" because it began in the middle Mississippi River valley, between St. Louis and Vicksburg. This culture spread over most of the Southeast.

See also: Article on Nectarines. NECTARINES. A nectarine is a fuzzless variety of p each. It is NOT a cross between a peach and a plum. Nectarines, like peaches, probably originated in China over 2,000 years ago and were cultivated in ancient Persia, Greece and Rome.
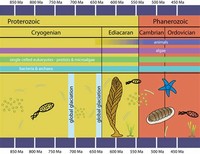
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from . It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran Periods. It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era and succeeded by the Paleozoic era.

The Paleoarchean (/ ˌ p eɪ l i oʊ ɑːr ˈ k iː ə n /), also spelled Palaeoarchaean (formerly known as early Archean), is a geologic era within the Archaean Eon. It spans the period of time —the era is defined chronometrically and is not referenced to a specific level of a rock section on Earth.

Paleoproterozoic Era, spanning the time period from 2,500 to 1,600 million years ago, is the first of the three sub-divisions of the Proterozoic Eon. It was during this era that the continents first stabilized. Paleontological evidence suggests that the Earth's rotational rate during this era resulted in 20 hour days ~1.8 billion years ago, implying a total of ~450 days per year.

The History of Pennsylvania begins in 1681 when William Penn received a royal charter from King Charles II of England, although human activity in the region precedes that date. The area was home to the Lenape, Susquehannock, Iroquois, Erie, Shawnee, Arandiqiouia, and other American Indian tribes.
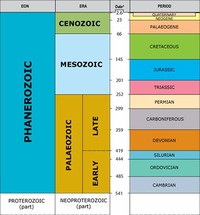
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current geologic eon in the geologic time scale, and the one during which abundant animal and plant life has existed. It covers 541 million years to the present, and began with the Cambrian Period when diverse hard-shelled animals first appeared.

The Pliocene ( / ˈ p l aɪ ə ˌ s iː n /; also Pleiocene) Epoch is the epoch in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58 million years BP. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch.

The Proterozoic Eon extended from 2500 Ma to 541 Ma (million years ago), and is the most recent part of the Precambrian Supereon. It can be also described as the time range between the appearance of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere and the appearance of first complex life forms (like trilobites or corals).
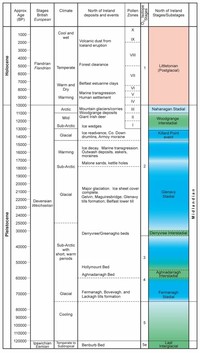
The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.588 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today). The informal term "Late Quaternary" refers to the past 0.5–1.0 million years.

Tertiary education, also referred to as third stage, third level, and postsecondary education, is the educational level following the completion of a school providing a secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including universities as well as trade schools and colleges.

The Ypresian shares its name with the Belgian Ieper Group (French: Groupe d'Ypres), which has an Ypresian age. The base of the Ypresian stage is defined at a strong negative anomaly in δ 13 C values at the PETM. The official reference profile for the base of the Ypresian is the Dababiya profile near the Egyptian city of Luxor.