Types of Hominids

The Hominidae (/ h ɒ ˈ m ɪ n ɪ d iː /), whose members are known as great apes or hominids, are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: Pongo, the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan; Gorilla, the eastern and western gorilla; Pan, the common chimpanzee and the bonobo; and Homo, which includes modern humans and its extinct relatives (e.g., the Neanderthal), and ancestors, such as Homo erectus.

Ardipithecus is a genus of an extinct hominine that lived during Late Miocene and Early Pliocene in Afar Depression, Ethiopia. ... Like most hominids, ...

A hominid is a member of the family Hominidae, the great apes: orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans. A hominine is a member of the subfamily Homininae: gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans (excludes orangutans). A hominin is a member of the tribe Hominini: chimpanzees and humans.

A hominoid, commonly called an ape, is a member of the superfamily Hominoidea: extant members are the gibbons (lesser apes, family Hylobatidae) and the hominids. A hominid is a member of the family Hominidae, the great apes: orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans.

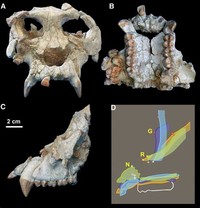
In the past, Gigantopithecus blacki (G. blacki) was thought to be closely related to early hominins, particularly Australopithecus, on the basis of molar evidence; this is now regarded a result of convergent evolution.

After Darwin, the family of Hominoids devised by scholars by the middle of the 20th century included two subfamilies: the subfamily of Hominids (humans and their ancestors) and that of Anthropoids (chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans). Those subfamilies were based on morphological and behavioral similarities in the groups: that's what the data had to offer, comparing skeletal differences.

But, we still need a way to discuss humans and their ancestors as a separate group, so researchers have proposed a further breakdown of the Homininae subfamily, to include Hominini (hominins or humans and their ancestors), Panini (pan or chimpanzees and bonobos), and Gorillini (gorillas).

The Hominidae (/ h ɒ ˈ m ɪ n ɪ d iː /), whose members are known as great apes or hominids, are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: Pongo, the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan; Gorilla, the eastern and western gorilla; Pan, the common chimpanzee and the bonobo; and Homo, which includes modern humans and its extinct relatives (e.g., the Neanderthal), and ancestors, such as Homo erectus.

As mentioned, Hominidae was originally the name given to the family of humans and their (extinct) close relatives, with the other great apes (that is, the orangutans, gorillas, and chimpanzees) all being placed in a separate family, the Pongidae.

The Hominidae (/ h ɒ ˈ m ɪ n ɪ d iː /), whose members are known as great apes or hominids, are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: Pongo, the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan; Gorilla, the eastern and western gorilla; Pan, the common chimpanzee and the bonobo; and Homo, which includes modern humans and its extinct relatives (e.g., the Neanderthal), and ancestors, such as Homo erectus.

Neanderthal expert Erik Trinhaus has long promoted the interbreeding hypothesis, but the theory really caught fire when a 2010 study published in Science magazine determined that Neanderthal DNA is 99.7 percent identical to modern human DNA (a chimp's is 99.8 percent identical).

A hominoid, commonly called an ape, is a member of the superfamily Hominoidea: extant members are the gibbons (lesser apes, family Hylobatidae) and the hominids. A hominid is a member of the family Hominidae, the great apes: orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans.

If Orrorin proves to be a direct human ancestor, then australopithecines such as Australopithecus afarensis ("Lucy") may be considered a side branch of the hominid family tree: Orrorin is both earlier, by almost 3 million years, and more similar to modern humans than is A. afarensis.

A hominoid, commonly called an ape, is a member of the superfamily Hominoidea: extant members are the gibbons (lesser apes, family Hylobatidae) and the hominids. A hominid is a member of the family Hominidae, the great apes: orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans.

Paranthropus (from Greek παρα, para "beside"; άνθρωπος, ánthropos "human") is a genus of extinct hominins.Also known as robust australopithecines, they were bipedal hominids that probably descended from the gracile australopithecine hominids (Australopithecus) 2.7 million years ago.

Paranthropus boisei or Australopithecus boisei or "Karl Surva" was an early hominin, ... Almost all primates and hominids are or were dietary generalists, ...

A partial cranium and mandible of Paranthropus robustus was ... Evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins notes "perhaps several different species" of robust hominids, ...
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as great apes or hominids, are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: Pongo, the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan; Gorilla, the eastern and western gorilla; Pan, the common chimpanzee and the bonobo; and Homo, which includes modern humans and its extinct relatives (e.g., the Neanderthal), and ancestors, such as Homo erectus.

an ape who's face has little air and whose hands have nails an… one of a subfamily of early hominids that lived between 4.2 mi… a gland that is located in the chest of the female mammal and…

Sahelanthropus tchadensis Brunet et al., 2002 Sahelanthropus tchadensis is an extinct homininae species and is probably the ancestor to Orrorin [citation needed] that is dated to about , during the Miocene epoch, possibly very close to the time of the chimpanzee–human divergence.

Retrieved from https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-a-hominin-reassessment-171252 Hirst, K. Kris. "What Is a Hominin?" ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-a-hominin-reassessment-171252 (accessed June 15, 2018).

Australopithecus is a confusing name with its hint of Australia ('southern land'), but these ape-men are southerners in a different sense. Their remains have been found in the southern hemisphere, and specifically in southern and eastern Africa.

Compared with modern Homo sapiens, which have only been around for the last 200,000 years, Homo erectus, or "upright man," had a long reign. The ancient ancestor of modern humans lived from 2 million years ago till about 100,000 years ago, possibly even 50,000 years ago.