Types of Inflammatory Disease

Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. In chronic hepatitis, liver inflammation continues for at least six months. This condition may be mild, causing relatively little damage, or more serious, causing many liver cells to be destroyed. Some cases lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.

Asthma is a chronic disease of the airways that makes breathing difficult. With asthma, there is inflammation of the air passages that results in a temporary narrowing of the airways that carry oxygen to the lungs.

Due to its powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic characteristics, bromelain is fantastic for reducing acute or chronic joint pain. The journal Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine published a research trial that evaluated 42 osteoarthritis patients with degenerative spine or painful joint conditions.
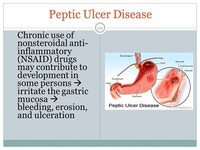
If you’ve been taking aspirin often and for a long time, you’re more likely to get a peptic ulcer. The same is true for other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs . They include ibuprofen and naproxen.

Harpagosides have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties. Since inflammation is linked to some forms of pain, some people use devil's claw to decrease pain from the following conditions:

Organic, grass-fed eggs are a fantastic food for quick and filling protein that is high in amino acids and nutrients. Unfortunately, if you are dealing with gut inflammation, leaky gut and autoimmune disease, eggs could be making your symptoms worse.

Eye disease related to Graves’ disease is called Graves’ ophthalmopathy. In more severe cases, one or both eyes may protrude from the eye sockets (also called the orbits). Graves’ disease causes an inflammatory response in the eye muscles; the muscles and tissues swell.

Inflammation from Hashimoto's disease, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, often leads to an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism). Hashimoto's disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States.
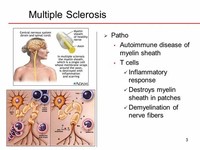
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is one of the most common diseases of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Today more than 2,300,000 people around the world have MS. MS is an inflammatory demyelinating condition.

Treatment strategies for periodontal disease currently include control of plaque biofilm and management of chronic inflammation with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). Novel classes of molecules may also promote resolution of inflammation; examples include resolvins and lipoxins, which have shown beneficial effects in animal models of periodontitis.

Gender also plays a role -- rheumatic diseases seem to affect women more than men. What to Expect When You Have a Rheumatic Disease • Osteoarthritis (OA) What it is: Unlike most rheumatic diseases, osteoarthritis isn’t linked to problems with your immune system. It results from damage to cartilage, the cushiony material on the end of your bones.

Overall infectious or inflammatory sinus disease can be broken up into acute (quick onset) or chronic (over a long period of time). Acute sinusitis is the most common form of sinusitis and is typically treated with a combination of antibiotics and agents to decrease inflammation in the nose. This type of infection typically resolves quickly over the course of a week or two. Surgery is ...

Lupus is a systemic autoimmune disease that occurs when your body's immune ... Overview of the clinical manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus in ...

Is tuberculosis an inflammatory disease? Our last research in experimental modelling demonstrates that the evolution from a latent infection to active disease requires a sudden infiltration of neutrophiles which promotes the extracellular growth of the bacilli.

Don't confuse turmeric with Javanese turmeric root (Curcuma zedoaria). How does it work? ... An inflammatory disease called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).

With type 2 diabetes, inflammation is internal. How Inflammation Develops. People with type 2 diabetes don't produce enough insulin or their bodies can't use the insulin adequately. Insulin is a hormone that is made by cells in the pancreas. It controls the amount of sugar in the blood. Insulin may also have an impact on tissue in the body.

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a disease that affects your large intestine, or colon. It causes irritation and swelling called inflammation. Eventually that leads to sores called ulcers in the lining there.

Willow bark comes from the willow tree (Salix species). The bark contains salicin, a compound chemically similar to aspirin. Salicin is metabolized in the body to salicylic acid, which is a precursor to aspirin. The herbal extract became popular as a remedy to relieve pain, inflammation, and fever. In the late 1800s, chemists discovered a way to make a synthetic version called acetylsalicylic acid, or aspirin.