Types of Liposarcoma

Liposarcoma is a cancer that arises in fat cells in deep soft tissue, such as that inside the thigh or in the retroperitoneum. Liposarcoma is a rare type of cancer that bears a resemblance to fat cells when examined under a microscope.

Whether you (or a loved one) are worried about developing a soft tissue sarcoma, have just been diagnosed, are going through treatment, or are trying to stay well after treatment, this detailed guide can help you find the answers you need.

Bone sarcomas The second large group of sarcoma is bone sarcomas or bone cancer. There are three types of bone sarcoma: osteosarcoma; Ewing’s sarcoma; and chondrosarcoma.

Chondrosarcoma. These tumors develop from cartilage cells. Ewing’s sarcoma. This subtype arises from very primitive cells in the body. It can start in either soft tissue or bone. Fibrosarcoma. This is cancer of fibrous tissue. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. These tumors arise out of nerves or related tissue outside of the brain and spinal cord.
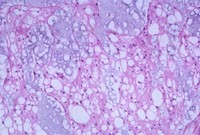
Chordoma is a rare type of cancer that occurs in the bones of the skull and spine. It is part of a family of cancers called sarcoma.
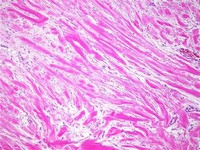
Desmoid-type fibromatosis (DF) is sometimes called Desmoid Tumour or aggressive fibromatosis. It is a rare type of benign (non-cancerous) tumour. DF develops from fibroblasts.

The cause of Ewing sarcoma is unknown. Though Ewing sarcoma arises from specific types of cells, it doesn't appear to be inherited. Risk factors. No clear risk factors for Ewing sarcoma are known. Complications. Ewing sarcoma can spread from where it started to other areas, making treatment and recovery more difficult.

Fibroblastic sarcoma includes: Malignant fibrous histiocytoma; Myxofibrosarcoma; Fibrosarcoma; Dermatofibrosarcoma; Fibroblastic sarcoma develops in the fibrous tissues within the body. It is most commonly found in the limbs, skin (dermofibrosarcoma) and in the trunk.

Liposarcoma is a cancer that arises in fat cells in deep soft tissue, such as that inside the thigh or in the retroperitoneum. Liposarcoma is a rare type of cancer that bears a resemblance to fat cells when examined under a microscope.
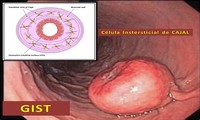
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) start in special cells in the wall of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, also known as the digestive tract. To understand GISTs, it helps to know something about the structure and function of the GI tract.

Liposarcoma. While there’s not ... Get Information on Leiomyosarcoma Cancer & Morcellators here. Get the medical and legal support you and your family deserve.

Liposarcoma is a malignant tumor that arises from mesenchymal cells (specifically, abnormal fat cells in deep soft tissue that multiply in an unregulated manner), mainly affecting middle-age people at sites such as the thigh, gluteal region, retroperitoneum, and leg and shoulder area.

Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) are sarcomas which originate from peripheral nerves or from cells associated with the nerve sheath, such as Schwann cells, perineural cells, or fibroblasts.
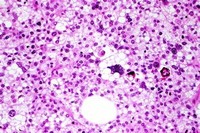
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) usually affects children in their first 5 years of life, but it is the most common type of RMS at all ages. The cells of ERMS look like the developing muscle cells of a 6- to 8-week-old embryo.

What is synovial sarcoma? Where does it happen in your body? Find out about its treatments, symptoms, and who's more likely to get it.

Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma Research. The Liddy Shriver Sarcoma Initiative is pleased to support UPS/MFH research. UPS is a rare tumor that usually affects adults. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. These treatments can increase survival but can also be very hard on the body.