Types of Memory Disorders

Acquired brain injury (ABI) is brain damage caused by events after birth, rather than as part of a genetic or congenital disorder such as fetal alcohol syndrome, perinatal illness or perinatal hypoxia.

Agnosia is the inability to process sensory information. Often there is a loss of ability to recognize objects, persons, sounds, shapes, or smells while the specific sense is not defective nor is there any significant memory loss.

Alzheimer's is a progressive disease, where dementia symptoms gradually worsen over a number of years. In its early stages, memory loss is mild, but with late-stage Alzheimer's, individuals lose the ability to carry on a conversation and respond to their environment.

Amnesia is the general term for a condition in which memory (either stored memories or the process of committing something to memory) is disturbed or lost, to a greater extent than simple everyday forgetting or absent-mindedness.

Symptoms: People with dementia with Lewy bodies often have memory loss and thinking problems common in Alzheimer's, but are more likely than people with Alzheimer's to have initial or early symptoms such as sleep disturbances, well-formed visual hallucinations, and slowness, gait imbalance or other parkinsonian movement features.

Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is a type of progressive dementia that leads to a decline in thinking, reasoning and independent function because of abnormal microscopic deposits that damage brain cells over time.

About frontotemporal dementia Arnold Pick, M.D., who described the first case of FTD. The nerve cell damage caused by frontotemporal dementia leads to loss of function in these brain regions, which variably cause deterioration in behavior and personality, language disturbances, or alterations in muscle or motor functions.
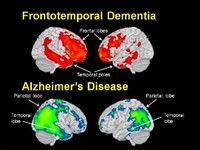
About frontotemporal dementia Arnold Pick, M.D., who described the first case of FTD. The nerve cell damage caused by frontotemporal dementia leads to loss of function in these brain regions, which variably cause deterioration in behavior and personality, language disturbances, or alterations in muscle or motor functions.

While there's no cure, the most effective treatment for HIV-associated dementia is HAART, which is known to reduce the amount of HIV in the blood. Particularly helpful drugs are ones that can cross the blood-brain barrier, like zidovudine .

Huntington’s disease is an inherited progressive neurodegenerative disorder, which affects muscle coordination and leads to general cognitive decline. If a parent carries the gene, there is a 50% chance of the child inheriting it.

Brad Williams has “hyperthymestic syndrome”—extraordinary autobiographical recall for daily life events. He has a diary-like recall of ordinary, daily events that most everyone else would have discarded, or at least relegated to memory storage not ordinarily accessible.

Korsakoff's syndrome, or Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, is a brain disorder caused by extensive thiamine deficiency, a form of malnutrition which can be precipitated by over-consumption of alcohol and alcoholic beverages compared to other foods.

Parkinson’s disease dementia first causes movement problems. Trouble with memory happens much later in the disease. Right now, there’s no cure for Lewy body dementia. But there are ways to ease symptoms for a while. Scientists are also getting better at understanding the differences between LBD and other conditions.

The term Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) refers to a syndrome that involves a gradual decline in mental abilities in the presence of preserved general cognitive function. The most common form of MCI involves a gradual difficulty with memory. Other patients can have gradual problems with language or problem solving.

Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) is a cause of progressive dementia that includes three primary symptoms: (1) progressive cognitive impairment, (2) gait and balance difficulties, and (3) urinary frequency and/or incontinence.

Parkinson's disease is the result of decreased stimulation of the motor cortex by the basal ganglia, usually due to the insufficient formation and action of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the neurons in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra.

Vascular dementia is widely considered the second most common cause of dementia after Alzheimer's disease, accounting for 10 percent of cases. Many experts believe that vascular dementia remains underdiagnosed — like Alzheimer's disease — even though it's recognized as common.

Symptoms: People with dementia with Lewy bodies often have memory loss and thinking problems common in Alzheimer's, but are more likely than people with Alzheimer's to have initial or early symptoms such as sleep disturbances, well-formed visual hallucinations, and slowness, gait imbalance or other parkinsonian movement features.

Memory Disorders At Upper Valley Medical Center, we offer patients comprehensive evaluation and advanced treatments paired with our experience in treating patients at all points on the memory-loss spectrum, including Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.