Types of Mollusks

Ammonoids are an extinct group of marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish) than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species.

Ammonoids are an extinct group of marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish) than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species.

Other articles where Aplacophora is discussed: mollusk: Annotated classification: Class Aplacophora Worm-shaped and without shells; marine, mostly in deep water. Possibly representive of the primitive molluscan condition or a secondary reduction from more advanced, shelled ancestors.

What is a bivalve mollusk? Bivalve mollusks (e.g., clams, oysters, mussels, scallops) have an external covering that is a two-part hinged shell that contains a soft-bodied invertebrate. A roughfile clam from the Flower Garden Bank National Marine Sanctuary—just one of many different bivalve mollusk species.

Bivalve mollusks (e.g., clams, oysters, mussels, scallops) have an external covering that is a two-part hinged shell that contains a soft-bodied invertebrate.

The cephalopods agree with the rest of the Mollusca in basic structure, and the ancestors appear to have the closest affinity with the ancestors of the class Gastropoda. The best-known feature of the cephalopods is the possession of arms and tentacles, eight or 10 in most forms but about 90 in Nautilus.

Cephalopods are the only mollusks with a closed circulatory system. Coleoids have two gill hearts (also known as branchial hearts) that move blood through the capillaries of the gills. A single systemic heart then pumps the oxygenated blood through the rest of the body.

Chiton, any of numerous flattened, bilaterally symmetrical marine mollusks, worldwide in distribution but most abundant in warm regions. The approximately 600 species are usually placed in the class Placophora, Polyplacophora, or Loricata (phylum Mollusca).

The mollusks or molluscs are the large and diverse phylum Mollusca,which includes a variety of familiar creatures well-known for theirdecorative shells or as seafood. These ra … nge from tiny snails,clams, and abalone to the octopus, cuttlefish and squid (which areconsidered the most intelligent invertebrates).

Cephalopods (squid, octopuses, cuttlefish) also possess a chitinous beak. Unlike the closely related annelids, mollusks lack body segmentation. Development passes through one or two trochophore stages, one of which (the veliger) is unique to the group.

A few gastropod types (such as conch, abalone, limpets, and whelks) are used as food, and several different species may be used in the preparation of escargot. Very few gastropod species transmit animal diseases; however, the flukes that cause human schistosomiasis use gastropods as intermediate hosts.

Mollusca is a large phylum of invertebrate animals whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (/ ˈ m ɒ l ə s k /). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species.

Kimberella is a monospecific genus of bilaterian known only from rocks of the Ediacaran period. The slug-like organism fed by scratching the microbial surface on which it dwelt in a manner similar to the gastropods, although its affinity with this group is contentious.

Monoplacophoran, (class Tryblidia), any of a group of primitive marine mollusks characterized by a single, cap-shaped shell and bilateral symmetry. The term Tryblidia is preferred over Monoplacophoran and Galeroconcha, because both latter terms are taken to include several fossil groups of uncertain relationships.

Octopus: Octopus, in general, any eight-armed cephalopod mollusk of the order Octopoda. The true octopuses are members of the genus Octopus, a large group of widely distributed shallow-water cephalopods. Learn more about the anatomy, behavior, and reproduction of octopuses in this article.

However, an analysis in 2009 using both morphological and molecular phylogenetics comparisons concluded the molluscs are not monophyletic; in particular, Scaphopoda and Bivalvia are both separate, monophyletic lineages unrelated to the remaining molluscan classes; the traditional phylum Mollusca is polyphyletic, and it can only be made monophyletic if scaphopods and bivalves are excluded.

Mollusca is a large phylum of invertebrate animals whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (/ ˈ m ɒ l ə s k /). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species.

Scallops are in the phylum Mollusca, a group of animals that also includes snails, sea slugs, octopuses, squid, clams, mussels, and oysters. Scallops are one of a group of mollusks known as bivalves. These animals have two hinged shells that are formed of calcium carbonate.
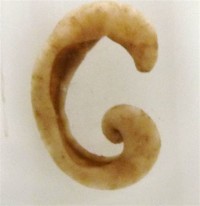
Solenogaster, small, wormlike, marine mollusk of the class Aplacophora (subclass Neomeniomorpha). Unlike most other mollusks, solenogasters have no shell. The body is covered instead by a cuticle containing many calcareous spicules.

Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish and octopus, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species.

Tentaculites is included in the order Tentaculitida, which along with the order Dacryoconarida belong to the class Tentauclitoidea. Hence, the proper designation for representatives of this class is tentaculitoids. The mode of life of tentaculitoids remains a matter of speculation.

Tusk shell, also called elephant’s tusk, elephant’s tooth, or tooth shell, any of several marine mollusks of the class Scaphopoda. There are four genera of tusk shells (Dentalium is typical and most common) and more than 350 species.

Nicholas Butterfield, who opposes the idea that Wiwaxia was a mollusc, has written that earlier microfossils from are fragments of a genuinely mollusc-like radula. This appears to contradict the concept that the ancestral molluscan radula was mineralized.

The mollusc (or mollusk /ˈmɒləsk/) composes the large phylum Mollusca of invertebrate animals. Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms.