Types of ms

LEMTRADA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Because of its risks, LEMTRADA is generally used in people who have tried 2 or more MS medicines that have not worked well enough.

Bladder Problems; Sexual Problems; Bowel ... People with MS may find that bladder and bowel symptoms prevent them ... Managing Symptoms in MS: Bladder Dysfunction ...
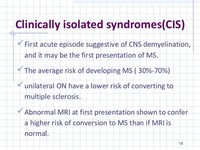
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) is one of the MS disease courses. CIS refers to a first episode of neurologic symptoms that lasts at least 24 hours and is caused by inflammation or demyelination (loss of the myelin that covers the nerve cells) in the central nervous system (CNS).

Tecfidera (dimethyl fumarate, or DMF) is an oral formulation approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for relapsing-remitting forms of multiple sclerosis (MS).

Seizures, which are the result of abnormal electrical discharges in an injured or scarred area of the brain, are fairly uncommon among people with MS. Their incidence has been estimated at 2-5 percent, compared to the estimated 3 percent incidence of seizures in the general population.

Fingolimod (INN, trade name Gilenya, Novartis) is an immunomodulating drug, mostly used for treating multiple sclerosis (MS). It has reduced the rate of relapses in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis by approximately one-half over a two-year period.

Glatiramer acetate. Glatiramer acetate (also known as Copolymer 1, Cop-1, or Copaxone - as marketed by Teva Pharmaceuticals) is an immunomodulator drug currently used to treat multiple sclerosis. It is a random polymer of four amino acids found in myelin basic protein, namely glutamic acid, lysine, alanine, and tyrosine.

Mitoxantrone is a potent drug related to those used in chemotherapy and similar to drugs used for acute leukemia and lymphomas.

Spasticity refers to feelings of stiffness and a wide range of involuntary muscle spasms (sustained muscle contractions or sudden movements). It is one of the more common symptoms of MS. Spasticity may be as mild as the feeling of tightness of muscles or may be so severe as to produce painful, uncontrollable spasms of extremities, usually of the legs.

Natalizumab is used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and Crohn's disease. It is co-marketed by Biogen and Élan as Tysabri, and was previously named Antegren. Natalizumab is administered by intravenous infusion every 28 days.

Find information about OCREVUS® (ocrelizumab), a prescription medicine used to treat adults with relapsing or primary progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. What is OCREVUS?

A common symptom of multiple sclerosis is some form of muscular paralysis. The term, 'paralysis', understandably tends to strike fear into the heart of anyone who has to face up to the possibility that one day they may have to face it.

The treatment of pressure sores becomes more difficult as the sore advances in severity. A Stage 1 sore is usually well managed by eliminating the source of the pressure. This should result in a rapid resolution of the early pressure sore. Stage 2 sores can be treated by medication and protective coverings, under the advice of a physician or wound specialist who may be a nurse of physician.

PPMS is characterized by worsening neurologic function (accumulation of disability) from the onset of symptoms, without early relapses or remissions.

Progressive-relapsing multiple sclerosis (PRMS) was described in the 1996 disease-course definitions as — steadily worsening neurologic function from the beginning with occasional relapses.

Relapsing-remitting MS is defined by inflammatory attacks on myelin (the layers of insulating membranes surrounding nerve fibers in the central nervous system (CNS)), as well as the nerve fibers themselves.

SPMS follows an initial relapsing-remitting course. Most people who are diagnosed with RRMS will eventually transition to a secondary progressive course in which there is a progressive worsening of neurologic function (accumulation of disability) over time.

Teriflunomide (trade name Aubagio, marketed by Sanofi) is the active metabolite of leflunomide. Teriflunomide was investigated in the Phase III clinical trial TEMSO as a medication for multiple sclerosis (MS).