Types of Oligopoly

Oligopoly II: Entry barriers Summary In this LP, we learn about how oligopolists can collude in order to maximise their profits, even though this agreement will not likely last.

An oligopoly is a market structure in which a few firms dominate. When a market is shared between a few firms, it is said to be highly concentrated. Although only a few firms dominate, it is possible that many small firms may also operate in the market.

The concept of oligopoly can be defined as under: “Oligopoly is that situation in which a firm bases its markets policy in part on the expected behaviour of a few close rivals.” – J. Stigier “An oligopoly is a market of only a few sellers, offering either homogeneous or differentiated products.

Mutual interdependence is a characteristic of an oligopoly. An oligopoly is a form of market. In oligopolies, the number of oligopolists, the sellers or producers, is limited.
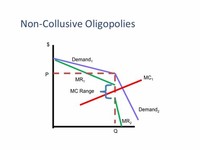
A-Level (AS and A2) Economics revision section covering Collusive and Non-Collusive Oligopolies, Price Fixing and Collusion, Price Leadership and Collusion, Non-Collusive Oligopoly, Oligopolies, Non-Price Competition and Price Wars Entry Barriers

Absence of price competition stems from product differentiation. In the case of a differentiated oligopoly, one finds non-price competition. W.J. Baumol, in his sales maximization theory, argues that in the real world non-price competition is the typical form of competition in oligopoly market.
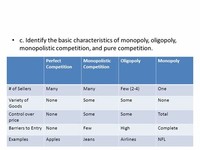
On the basis of product differentiation, oligopoly may be classified as Pure or Perfect Oligopoly and Imperfect or Differentiated Oligopoly. In the case of pure oligopoly, the product of different firms in the industry is identical or homogeneous while in the case of differentiated oligopoly, the products of different firms are not identical but rather differentiated products.