Types of Political Ideologies

Absolutism, the political doctrine and practice of unlimited centralized authority and absolute sovereignty, as vested especially in a monarch or dictator. The essence of an absolutist system is that the ruling power is not subject to regularized challenge or check by any other agency, be it judicial, legislative, religious, economic, or electoral.

Political anarchism makes all those philosophical claims, AND the further claim that we should try and overthrow the current State. It is consequently a more extreme position. Anarchism can be further sub divided into right-wing and left-wing anarchism, with each side disagreeing about the moral status of property.

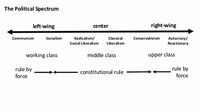
Political ideology is a term fraught with problems, having been called "the most elusive concept in the whole of social science". However, ideologies tend to identify themselves by their position on the political spectrum (such as the left, the centre or the right), though this is very often controversial.
Typically, each ideology contains certain ideas on what it considers to be the best form of government (e.g. democracy or autocracy) and the best economic system (e.g. capitalism or socialism). Sometimes the same word is used to identify both an ideology and one of its main ideas.

The ideologies of capitalism and socialism are the two sides of a counterfeit coin. We ought to discourse in other terms, employing some moral imagination and confronting honestly our disorders, public and private, at the close of the 20th century.

Communism, political and economic doctrine that aims to replace private property and a profit-based economy with public ownership and communal control of at least the major means of production (e.g., mines, mills, and factories) and the natural resources of a society.

Conservative policies generally emphasize empowerment of the individual to solve problems. Check out our page: 2016 Presidential Election resources for teachers. NOTE: The terms “left” and “right” define opposite ends of the political spectrum.

In social studies, a political ideology is a certain set of ethical ideals, principles, doctrines, myths or symbols of a social movement, institution, class or large group that explains how society should work and offers some political and cultural blueprint for a certain social order.

Environmentalism or environmental rights is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement regarding concerns for environmental protection and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seeks to incorporate the impact of changes to the environment on humans, animals, plants and non-living matter.

Prior to Fascism's accommodation of the political right, Fascism was a small, urban, northern Italian movement that had about a thousand members. After Fascism's accommodation of the political right, the Fascist movement's membership soared to approximately 250,000 by 1921.

Liberal policies generally emphasize the need for the government to solve problems. Conservatives believe in personal responsibility, limited government, free markets, individual liberty, traditional American values and a strong national defense. Believe the role of government should be to provide people the freedom necessary to pursue their own goals. Conservative policies generally emphasize empowerment of the individual to solve problems.

Nationalism, ideology based on the premise that the individual’s loyalty and devotion to the nation-state surpass other individual or group interests. Nationalism is a modern movement.

Political Ideology. Political ideology is a set of values and beliefs held by groups regarding the purpose and scope of government. Core political ideologies like conservatism, liberalism, and socialism, shape an individual's stance on the government's role in economic and social issues.