Types of Project Management

"The co-project manager model is unique to APF," Wysocki notes, "and is a critical success factor for such projects. The most important characteristic is that both parties are equally vested and responsible for the project." Another unique characteristic of the Adaptive Framework is its approach to requirements definition.

Agile project management is a value-driven approach that enables Project Managers to deliver high-priority, high-quality work. Agile project management is a value-driven approach that enables Project Managers to deliver high-priority, high-quality work.

Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is a project management methodology introduced in 1997 by Eliyahu (Eli) M. Goldratt. It applies Goldratt's Theory of Constraints (TOC) to resolve project task and delivery issues.

Critical path project management (CPM) is a technique used to complete projects on time by focusing on key tasks. One path through all the inter-connected tasks is the fastest avenue to take when completing any project.

Extreme programming (XP) is a software development methodology which is intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. As a type of agile software development, it advocates frequent "releases" in short development cycles, which is intended to improve productivity and introduce checkpoints at which new customer requirements can be adopted.

Read or Download Project Management 101: The Complete Guide to Agile, Kanban, Scrum and Beyond from our The Ultimate Guide to Project Management e-book for FREE and start learning today!

Scrum project management is a methodology for managing software delivery that comes under the broader umbrella of agile project management. It provides a lightweight process framework that embraces iterative and incremental practices, helping organizations deliver working software more frequently.

There must be a management decision before the project starts if it should be agile or traditional. Certainly, agile project is not fit for certain types of projects, vice versa. Traditional waterfall projects can fail, so can agile projects.

Definition of Lean Project Management Companies work on various projects that include developing products, services, and/or processes. Lean Project Management uses data-driven methods to manage projects by focusing on continuously improving the process.

New Product Development (NPD) and New Product Introduction (NPI) is the process of bringing a product or service from inception to market. Pre-release steps are generally referred to as New Product Development, and the release to manufacturing and market steps are referred to as New Product Introduction.

Project management, then, is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. It has always been practiced informally, but began to emerge as a distinct profession in the mid-20th century.

PRINCE2 Definition. PRINCE2 (an acronym for PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is a de facto process-based method for effective project management. Used extensively by the UK Government, PRINCE2 is also widely recognised and used in the private sector, both in the UK and internationally.
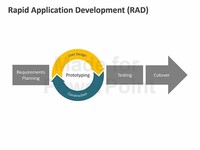
Unsuitable for RAD - Many people must be involved in the decisions on the project, the decision makers are not available on a timely basis or they are geographically dispersed. project team Suitable for RAD - The project team is small (preferably six people or less).
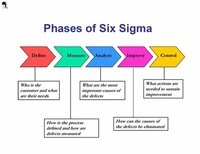
Six Sigma tools such as combinatorial methods and Markov chains can be applied to improvement of testing processes. Risk Management – Six Sigma tools such as Monte Carlo simulation (if not already being used) can find application within the context of professional project management.