Types of Protists

Amoeba can change shape and move around by extending their pseudopodia, or 'false feet.' Paramecium move by using the cilia, or tiny hair-like structures, that cover their entire bodies. Paramecium bursaria form symbiotic relationships with green algae, according to Kenyon College's MicrobeWiki.

Protists are responsible for a variety of human diseases including malaria, sleeping sickness, amoebic dysentery and trichomoniasis. Malaria in humans is a devastating disease. It is caused by five species of the parasite Plasmodium, which are transmitted to humans by female Anopheles mosquitoes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

Ascophyllum nodosum is a large, common brown alga (Phaeophyceae) in the family Fucaceae, being the only species in the genus Ascophyllum. It is seaweed of the northern Atlantic Ocean, also known as rockweed, Norwegian kelp, knotted kelp, knotted wrack or egg wrack.

Species- Fucus vesiculosus. Domain - Eukaryotic All organisms within this domain have a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Kingdom - Chromista Chromista translates into the word "colored." Organisms within this kingdom are mostly photosynthetic.

Their proposal was to refer to Blastocystis from humans and animals as Blastocystis sp. subtype nn where nn is a number assigned to each group according to the degree of genetic identity of the Blastocystis organisms, based on gene sequences, rather than the host that was infected.

An Amoeba proteus, left, with a Paramecium bursaria. Amoeba can change shape and move around by extending their pseudopodia, or 'false feet.' Paramecium move by using the cilia, or tiny hair-like structures, that cover their entire bodies. Paramecium bursaria form symbiotic relationships with green algae, according to Kenyon College's MicrobeWiki.

Caulerpa taxifolia. Caulerpa taxifolia is a species of seaweed, an alga of the genus Caulerpa. Native to the Indian Ocean, it is widely used ornamentally in aquariums, because it is considered attractive and neat in arrangement, and is easy to establish and care for.

Caulerpa taxifolia. Caulerpa taxifolia is a species of seaweed, an alga of the genus Caulerpa. Native to the Indian Ocean, it is widely used ornamentally in aquariums, because it is considered attractive and neat in arrangement, and is easy to establish and care for.

Start studying Protists & Fungi Key Questions. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.

Crithidia are members of the trypanosome protozoa. They are parasites that exclusively parasitise arthropods, mainly insects. They pass from host to host as cysts in infective faeces and typically, the parasites develop in the digestive tracts of insects and interact with the intestinal epithelium using their flagellum.

Cryptomonads are photosynthetic flagellates, mostly pretty small. (The above image shows Geminigera, from the Tree of Life website: Geminigera | Plagioselmis | Teleaulax). But each cryptomonad contains chloroplasts wrapped in, not two, but four membranes—and each cryptomonad chloroplast contains a DNA-containing structure called a nucleomorph.

Cyclospora cayetanensis. Cyclospora cayetanensis is a protozoan that causes disease in humans, and perhaps primates. It has been linked in the United States to fecally contaminated imported produce, and was virtually unknown before about 1990, but has been on the rise since.

Dientamoeba fragilis (D. fragilis)is a trichomonad (a genus of anaerobic protists that are parasites of vertebrates) parasite found in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and implicated as a cause of gastrointestinal disease. D. fragilis has been found in most parts of the world in both rural and cosmopolitan areas.
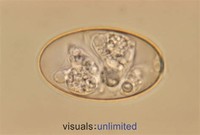
Eimeria, genus of parasitic protozoans of the spore-producing phylum Apicomplexa (previously Sporozoa). Eimeria, which causes coccidiosis in livestock and wild animals, infects mainly the cells of the digestive tract, although it also attacks cells of the liver and the bile duct.
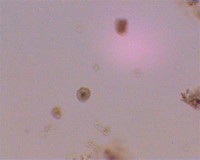
Quick Answer. Doses of metronidazole, nitazoxanide and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole have been shown to treat infections of Edolimax nana that cause gastrointestinal distress, such as acute diarrhea, according to Case Reports in Gastroenterology.

Entamoeba histolytica. Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic amoebozoa, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates causing amoebiasis, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 50 million people worldwide.
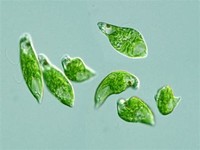
As photosynthetic protists, Euglena have a taxonomy that is somewhat contentious, and the genus is often placed either in the phylum Euglenozoa or the algal phylum Euglenophyta. Euglena Euglena gracilis (highly magnified) in fresh water.

A number of forams have unicellular algae as endosymbionts, from diverse lineages such as the green algae, red algae, golden algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates. Some forams are kleptoplastic, retaining chloroplasts from ingested algae to conduct photosynthesis.

White spot disease (Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, or Ich) is one of the most common parasitic diseases affecting tropical fish. It is also, unfortunately, a very persistent disease. White spot is caused when a protozoan attacks and attaches itself to a fish's body, fins, and gills.

Though it resembles a tall grass, giant kelp is not a plant. Instead, it is a brown alga and is part of the large kingdom of life known as the Protista. Most protists are single-celled organisms, but the giant kelp is a complex species and is the largest protist in the world.

The chloroplasts are pigmented similarly to those of the heterokonts, but the structure of the rest of the cell is different, so it may be that they are a separate line whose chloroplasts are derived from similar red algal endosymbionts.

Hijiki comes in two forms mostly: regular hijiki, which is rather twig-like in dried form, and me hijiki, small buds of hijiki that looks like black tea in dried form. Once regular hijiki is reconstituted, it looks like long black noodles. Star Trek fans may see a remarkable similarity to gagh. However hijiki does not move on your plate or have feet. The traditional way to cook hijiki is to ...

Iodamoeba bütschlii is a species of amoeba. It gets its name from its appearance when stained with iodine. Named for Otto Bütschli by Prowazek in 1912, Iodamoeba bütschlii is a nonpathogenic parasitic ameba, commonly found in the large intestines of people, pigs and other mammals. The distribution of I. bütschlii is worldwide.

Protists are typically divided into three categories, including animal-like protists, plant-like protists, and fungus-like protists. Protists vary in how they move, which can range from cilia, flagella, and psuedopdia. In other words, protists move by microscopic hair that flaps together, by a long tail that moves back and forth, or by extending its cell body, similar to an amoeba.

Laminaria is a genus of 31 species of brown algae commonly called "kelp". Some species are also referred to as tangle. This economically important genus is characterized by long, leathery laminae and relatively large size.

Lake Akan is home to Marimo often reaching the size of 20 cm - 30 cm, the largest known marimo in the world. The structure of the lake-balls is unique.

Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that have the ability to conduct photosynthesis. Certain algae are familiar to most people; for instance, seaweeds (such as kelp or phytoplankton), pond scum or the algal blooms in lakes.

Neospora is a genus of important pathogens in cattle and dogs. It was not discovered until 1984 in Norway, where it was found in dogs. It is highly transmissible and some herds can have up to a 90% prevalence.

Shown here growing near Kaikōura, bull kelp or rimurapa is the dominant seaweed of exposed rocky coasts around New Zealand and the subantarctic islands. Its thick flexible stipe supports a spongy broad blade that is usually divided into narrow straps.

Paramecia are single-celled protists that are naturally found in aquatic habitats. They are typically oblong or slipper-shaped and are covered with short hairy structures called cilia. Certain paramecia are also easily cultured in labs and serve as useful model organisms.

Paramecium, showing contractile vacuole and ciliary motion. Paramecium lives in fresh water. The excess water it takes in via osmosis is collected into two contractile vacuoles, one at each end, which swell and expel water through an opening in the cell membrane. The sweeping motion of the hair-like cilia helps the single-celled organism move.

Physarum polycephalum, literally the "many-headed slime", is a slime mold that inhabits shady, cool, moist areas, such as decaying leaves and logs. Like slime molds in general, it is sensitive to light; in particular, light can repel the slime mold and be a factor in triggering spore growth.

The genus Plasmodium causes malaria, one of the greatest scourges of humans. There are 4 species that infect humans of which Plasmodium falciparum is the most dangerous. Malaria has probably caused more human deaths than any other infectious disease; even today it is estimated to kill a million people a year in the sub-Saharan Africa.

The potato famine in Ireland which was caused by the potato blight killed in the region of 2 million people out of a pre-famine population of 9 million, and it started emigrat … ion to America, Canada, Australia and other places, displacing another one million during the famine, and many more since.

a form of malaria, caused by the protozoan Plasmodium malariae, characterized by febrile paroxysms that occur every 72 hours. Also called quartan fever. Compare falciparum malaria, tertian malaria.

Introduction to the Radiolaria. With their glassy skeletons of often perfect geometric form and symmetry, radiolarians are among the most beautiful of all protists. They are also an ancient group, going back all the way to the early Cambrian Period. Their abundance in many rocks, their long geologic history, and their diversity through time make them important sources of information on the geologic age and structure of many deposits.

The Rhizaria are a species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular[1] eukaryotes.[2] A multicellular form has also been described.[3] This supergroup was proposed by Cavalier-Smith in 2002.

No one has contributed a brief summary to this page yet. Explore what EOL knows about Saccharina sculpera.. Add a brief summary to this page

Sargassum is a genus of brown (class Phaeophyceae) macroalgae in the order Fucales. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral reefs, and the genus is widely known for its planktonic (free-floating) species.

sea lettuce is a PROTIST! it is an algae, which is considered a subkingdom or sorts in the kingdom Eukarya. they are plant-like as opposed to protozoa which are animal-like protists.

Theileria parva is a species of parasites, named in honour of Arnold Theiler, that causes East Coast fever (theileriosis) in cattle, a costly disease in Africa. The main vector for T. parva is the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus.

…tract caused by a protozoan, Trichomonas vaginalis; males usually have no symptoms with this infection, and only a portion of infected females have a vaginal discharge. …is caused by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis, frequently resident in the vagina. Chemical irritants or the spread of ...

Trypanosoma brucei is a species of parasitic kinetoplastid belonging to the genus Trypanosoma. The parasite is the cause of a vector-borne disease of vertebrate animals, including humans, carried by genera of tsetse fly in sub-Saharan Africa.

Just like many other protists, the Trypanosoma cruzi has a cytostome. The cytostome is a mouth-like opening through which food passes. The opening of the cytostome usually has a diameter of up to 0.3 µm. However, it can be shorter in the deeper portion. Macromolecules are concentrated in reservosome.

Trypanosoma is a genus of kinetoplastids (class Kinetoplastida), a monophyletic[1] group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa.

Is it a plant? An animal? A protist? Volvox is a confusing little organism with features that make it seem like all three. This lesson will...

Why is seaweed a protist and not a plant? seaweed does not have roots like other plants. seaweed does not have proper leaves like most plants. seaweed has a different cellular arrangement without a cellulose cel … l wall and do not have differentiated tissues. seaweed uses a different type of chlorophyll the protist kingdom is mostly made up of the misfits that doesn't exactly meat other ...

Not all snow algae color snow pink. Green snow can be found in layers below the surface if you shovel into it, usually near tree canopies in alpine forests. One of these algae, Green snow can be found in layers below the surface if you shovel into it, usually near tree canopies in alpine forests.