Types of Psychology Studies

Behavioral Psychology Defined. Behavioral psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on the study and alteration of people's behaviors, including their actions, emotions and thoughts. There are four recognized sub-disciplines of behavioral psychology: applied behavior analysis, behavior therapy, cognitive therapy and cognitive-behavior therapy.

A closely related specialty is pediatric psychology; pediatric psychologists work in medical settings. Child psychologists may work in outpatient centers, government agencies, or hospitals. Some are in private practice. Child Psychologist Education and Training. Child psychology is a sub-specialty of clinical psychology.

Clinical psychology became more established during the period of World War I as practitioners demonstrated the usefulness of psychological assessments. In 1917, the American Association of Clinical Psychology was established, although it was replaced just two years later with the establishment of the American Psychological Association (APA).

Cognitive psychology is the branch of psychology that focuses on the way people process information. It looks at how we process information we receive and how the treatment of this information leads to our responses.

Community psychologists analyze the mental health of communities as a whole. In this lesson, we will discuss the field of community psychology, examine some of the areas in which community psychologists work and look at the overall goals of community psychology.

Such degree options include general psychology, industrial-organizational psychology, marketing, and consumer studies. If you are interested in becoming a consumer psychologist, focus on taking courses that will build your understanding of human behavior, marketing, social psychology, personality, and culture.

Video: Correlational Research: Definition, Purpose & Examples This lesson explores, with the help of two examples, the basic idea of what a correlation is, the general purpose of using correlational research, and how a researcher might use it in a study.
![Correlational Study[Edit]](/images/200_25/25d6fa9b9899b94e5242578f1a6a5efe.jpeg)
In psychology, correlational research determines if a relationship exists between two or more variables, and if so, to what degree the relationship occurs. There are three main types of correlational studies: natural observation, survey research, and archival research.
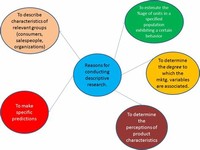
Descriptive research methods are pretty much as they sound -- they describe situations. They do not make accurate predictions, and they do not determine cause and effect. There are three main types of descriptive methods: observational methods, case-study methods and survey methods. This article will briefly describe each of these methods ...
![Descriptive Studies[Edit]](/images/200_0e/0ebb19016741032fa1f92f34413097e4.jpeg)
Descriptive research methods are pretty much as they sound — they describe situations. They do not make accurate predictions, and they do not determine cause and effect. There are three main types of descriptive methods: observational methods, case-study methods and survey methods.

Developmental psychologists study changes in human development across the lifespan, including physical, cognitive, social, intellectual, perceptual, personality and emotional growth. For Teachers An advanced degree in psychology is the foundation of many interesting career paths within the discipline.

Educational psychology is devoted to the study of how people learn including individual differences in learning, gifted learners, and learning disabilities. Educational psychology is devoted to the study of how people learn including individual differences in learning, gifted learners, and learning disabilities.

Engineering psychology is a field of psychology that focuses on the relationship between humans and the products that we use everyday. Specialists in this field concentrate on exploring the relationships between man and machine, so to speak.

Psychology is the scientific study of people's thoughts, behaviors, and feelings. Shannon's question about learning is part of psychology. Because psychology is a science, many of its big questions (like 'How do humans learn?') are tested through experiments, or carefully designed procedures to answer a question or test a hypothesis.
![Experiments[Edit]](/images/200_c9/c9786b18fe3c64cff560cfd3038642c4.jpeg)
Experimental psychologists use science to explore the processes behind human and animal behavior.

Forensic psychology is the interaction of the practice or study of psychology and the law. Psychologists interested in this line of applied work may be found working in prisons, jails, rehabilitation centers, police departments, law firms, schools, government agencies, or in private practice, to name a few.

Humanistic psychology holds that people are naturally good. This field integrates person-centered therapy to obtain qualitative data specific to each individual. This field integrates person-centered therapy to obtain qualitative data specific to each individual.
![Idiographic (Qualitative Approach)[Edit]](/images/200_67/6760ea25dc5c30755dc5514a59649f65.jpeg)
Psychologists who adopt this approach are mainly concerned with studying what we share with others. That is to say in establishing laws or generalizations. The term “idiographic” comes from the Greek word “idios” meaning “own” or “private”.

Holistic psychotherapy utilizes traditional and non-traditional therapies of holistic healing with the purpose of creating an integration of the mind, body and spirit. The idea combines a broad range of different holistic approaches to help the patient reach the deepest level of healing possible.
![Naturalistic Observation[Edit]](/images/200_cb/cb801f89fe724ab0b33dfef908f71312.jpeg)
Naturalistic observation is a method of observing people in their normal environment. From simple college studies to clinical trials, there are a variety of examples of naturalistic observation. Other methods often lead to artificial changes in subjects' behaviors.
![Nomothetic (Quantitative Approach)[Edit]](/images/200_5e/5e4dd95df45d6e32ac6191c14dd0f450.jpeg)
The term “nomothetic” comes from the Greek word “nomos” meaning “law”. Psychologists who adopt this approach are mainly concerned with studying what we share with others. That is to say in establishing laws or generalizations.

Freud’s psychoanalysis is both a theory and therapy. Sigmund Freud (writing between the 1890s and the 1930s) developed a collection of theories which have formed the basis of the psychodynamic approach to psychology.
![Self Report[Edit]](/images/200_d0/d0774adb3e656a4591dc3a72a887caf8.jpeg)
Data from these questionnaire can be used to identify relationships between scores on the variable(s) that the questionnaire is assumed to measure and either performance on behavioural tasks, physiological measures taken during an experiment, or even scores obtained from other questionnaires (some studies just report on the correlations between batches of self-report measures!). Self-report measures are popular for a number of reasons.
![Statistics[Edit]](/images/200_a9/a93a1d82beb4739087b09010c8c68d31.jpeg)
Psychology is a science, which means that in order to understand people's thoughts and behaviors, a basic understanding of statistics is necessary. Most psychology studies use inferential statistics. This lesson covers basic types of inferential statistics, as well as how to decide whether a hypothesis was supported by the results.