Types of Random Sampling

An example of cluster sampling is area sampling or geographical cluster sampling. Each cluster is a geographical area. Because a geographically dispersed population can be expensive to survey, greater economy than simple random sampling can be achieved by grouping several respondents within a local area into a cluster.

The multistage sampling is a complex form of cluster sampling. The cluster sampling is yet another random sampling technique wherein the population is divided into subgroups called as clusters; then few clusters are chosen randomly for the survey.

A simple random sample is a subset of a statistical population in which each member of the subset has an equal probability of being chosen. An example of a simple random sample would be the names of 25 employees being chosen out of a hat from a company of 250 employees.
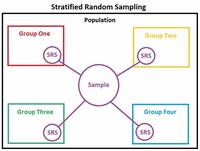
Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata. In stratified random sampling, or stratification, the strata are formed based on members' shared attributes or characteristics.

Systematic sampling is a type of probability sampling method in which sample members from a larger population are selected according to a random starting point and a fixed, periodic interval. This interval, called the sampling interval, is calculated by dividing the population size by the desired sample size.