Types of Spondylolisthesis

Spondylolisthesis is often defined in the literature as displacement in any direction. Yet, medical dictionaries usually define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it (or the sacrum).

Isthmic anterolisthesis is where there is a defect in the pars interarticularis. It is the most common form of spondylolisthesis; also called spondylolytic spondylolisthesis, it occurs with a reported prevalence of 5–7 percent in the US population.

This type of spondylolisthesis is most often seen in older patients. In Type III, degenerative spondylolisthesis there is no pars defect and the vertebral slippage is never greater than 30%. In Type III, degenerative spondylolisthesis there is no pars defect and the vertebral slippage is never greater than 30%.

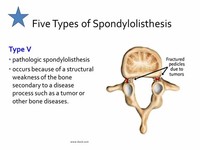
Type IV, traumatic spondylolisthesis, is associated with acute fracture of a posterior element (pedicle, lamina or facets) other than the pars interarticularis. Type V, pathologic spondylolisthesis, occurs because of a structural weakness of the bone secondary to a disease process such as a tumor or other bone disorder.
Start studying OMM M1.3 Exam 2: Spondylolisthesis II_LL. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.

Spondylolisthesis is defined as forward translation of a vertebral body with respect to the vertebra below. The term is derived from the Greek roots spondylo, meaning spine, and listhesis, meaning to slide down a slippery path.