Types of Stomach Infections

H. pylori is a common bacteria that may sometimes cause pain and may lead to ulcers. While an H. pylori infection can be normal, there are some instances where you should be concerned. Serious complications include internal bleeding and obstructions in your stomach. Learn about risk factors, complications, and more.

Campylobacter bacteria can get into your system if you eat undercooked poultry or you eat food that has touched raw or undercooked poultry. The bacteria usually live in the digestive systems of animals, including poultry and cattle. Unpasteurized milk can also have campylobacter bacteria. Campylobacteriosis usually develops in isolated cases. Sometimes, though, there can be an outbreak when several people have the same infection.
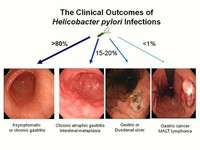
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a type of bacteria. These germs can enter your body and live in your digestive tract. After many years, they can cause sores, called ulcers, in the lining of your stomach or the upper part of your small intestine. For some people, an infection can lead to stomach cancer.

H. pylori is a bacteria that infects the stomach and small intestine and is the major cause of stomach and duodenal ulcers. Symptoms of H. pylori infection include frequent burping, bloating, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and weight loss. H. pylori infection can cause ulcers, gastritis and stomach cancer.

WebMD explains the causes, symptoms, and treatment of gastritis, a common condition in which the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed and irritated.

Gastroenteritis flu can be caused by many different kinds of viruses. The main types are rotavirus and norovirus. Rotavirus is the world's most common cause of diarrhea in infants and young children. Norovirus is the most common cause of serious gastroenteritis and also foodborne disease outbreaks in the U.S.

Your doctor may use ultrasound to eliminate other diseases. Upper endoscopy: This procedure involves passing a thin tube (endoscope) down the esophagus to examine the lining of the stomach. What Is the Treatment for Gastroparesis? Gastroparesis is a chronic (long-lasting) condition. This means that treatment usually doesn't cure the disease.

Cancer can also cause loss of appetite, particularly if it’s concentrated in the following areas: colon; stomach; ovaries; pancreas; Pregnancy can also cause a loss of appetite during the first trimester. Medications. Some medications and drugs may reduce your appetite.

Common abdominal causes of nausea include inflammation of the liver (hepatitis) or pancreas (pancreatitis); a blocked or stretched intestine or stomach; gastroesophageal reflux (GERD); irritation of the stomach, intestinal lining, appendix or pelvic organs; inflammation of the kidney; and gallbladder problems.

What is non-ulcer dyspepsia? Non-ulcer dyspepsia is sometimes called functional dyspepsia. It means that no known cause can be found for the symptoms. That is, other causes for dyspepsia such as duodenal ulcer, stomach ulcer, acid reflux and oesophagitis, inflamed stomach (gastritis) and eosinophilic oesophagitis are not the cause.

But when scientists discovered H. pylori in 1982, they found that the germs were the cause of most stomach ulcers. After H. pylori enters your body, it attacks the lining of your stomach, which usually protects you from the acid your body uses to digest food. Once the bacteria have done enough damage, acid can get through the lining, which leads to ulcers. These may bleed, cause infections, or keep food from moving through your digestive tract.

Shigella germs are in the stool (poop) of sick people while they have diarrhea and for up to a week or two after the diarrhea has gone away. Shigella germs are very contagious; it takes just a small number of Shigella germs to make someone sick.

While the infection is a major cause of stomach cancer, most people infected with H. pylori never develop stomach cancer. How are H. pylori infections treated? If you have an H. pylori infection that isn’t causing you any problems and you aren’t at increased risk of stomach cancer, treatment may not offer any benefits.

Amebiasis is a parasitic infection, common in the tropics and caused by contaminated water. Symptoms can be severe and usually start 1-4 weeks after exposure.

Yersiniosis is an infection caused most often by eating raw or undercooked pork contaminated with Yersinia enterocolitica bacteria. CDC estimates Y. enterocolitica causes almost 117,000 illnesses, 640 hospitalizations, and 35 deaths in the United States every year.