Types of Telecommunication
Many services offered over Bluetooth can expose private data or let a connecting party control the Bluetooth device. Security reasons make it necessary to recognize specific devices, and thus enable control over which devices can connect to a given Bluetooth device. At the same time, it is useful for Bluetooth devices to be able to establish a connection without user intervention (for example, as soon as in range).

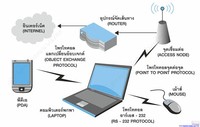
Telecommunication networks. Computer and Network Examples. A Telecommunications network is a network of nodes, links, trunks and telephone switches that are connected, operated by telephone companies and realize telephone, audio, visual and data communications among the users.

Telecommunications software is any type of software package that aids in the process of electronic communications, especially those that involve the transmission of audio in some manner.
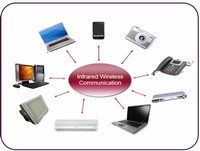
Infrared (IR) is a wireless mobile technology used for device communication over short ranges. IR communication has major limitations because it requires line-of-sight, has a short transmission range and is unable to penetrate walls.

Telecommunication devices are used to exchange data from one device to another using technology. There are many components of telecommunication devices such as input output, channel, processor etc. Some real life examples are mobile, refrigerator, washing machine, TV and radio systems etc.

Telecommunication is the transmission of signs, signals, messages, words, writings, images and sounds or information of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic systems. Telecommunication occurs when the exchange of information between communication participants includes the use of technology.

The DSL signal passes through a designated data jack, while over-the-phone discussion travels through the designated phone jack on the splitter. In most cases, the telephone company or service provider will install the splitters for you; however, you can also install one on your own.

A 1990s Ethernet network interface controller that connects to the motherboard via the now-obsolete ISA bus. This combination card features both a BNC connector (left) for use in (now obsolete) 10BASE2 networks and an 8P8C connector (right) for use in 10BASE-T networks.

Packet switching is used to optimize the use of the channel capacity available in digital telecommunication networks, such as computer networks, and minimize the transmission latency (the time it takes for data to pass across the network), and to increase robustness of communication.

In modern protocol design, protocols are layered to form a protocol stack. Layering is a design principle which divides the protocol design task into smaller steps, each of which accomplishes a specific part, interacting with the other parts of the protocol only in a small number of well-defined ways.

The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's circuit-switched telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators, providing infrastructure and services for public telecommunication.

There are two types of radio networks currently in use around the world: the one-to-many broadcast network commonly used for public information and mass media entertainment; and the two-way radio type used more commonly for public safety and public services such as police, fire, taxicabs, and delivery services.

Telecommunications is a universal term that is used for a vast range of information-transmitting technologies such as mobile phones, land lines, VoIP and broadcast networks. In telecommunications, data is transmitted in the form of electrical signals known as carrier waves, which are modulated into analog or digital signals for transmitting information.

In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel.

Telecommunication Processors: Telecommunication processors support data transmission and reception between the terminals and computers. Processors perform a variety of control and support functions in a telecommunication network.

Telecommunications, also known as telecom, is the exchange of information over significant distances by electronic means and refers to all types of voice, data and video transmission. This is a broad term that includes a wide range of information transmitting technologies such as telephones (wired and wireless), microwave communications, fiber optics, satellites, radio and television broadcasting, the internet and telegraphs.

Telecommunication is the transmission of signs, signals, messages, words, writings, images and sounds or information of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic systems. Telecommunication occurs when the exchange of information between communication participants includes the use of technology.