Types of Transformer

An autotransformer has a single winding with two end terminals, and one or more terminals at intermediate tap points, or it is a transformer in which the primary and secondary coils have part of, or all of their turns in common.

An Auto-transformer (sometimes called auto-step down transformer) is an electrical transformer with only one winding. The "auto" (Greek for "self") prefix refers to the single coil acting alone and not to any kind of automatic mechanism.
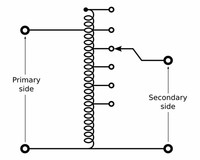
An auto transformer has higher efficiency than two winding transformer. This is because of less ohmic loss and core loss due to reduction of transformer material. Auto transformer has better voltage regulation as voltage drop in resistance and reactance of the single winding is less.

Transformer in loaded condition-temperature increases inside main tank,oil inside starts heating and expands the excessive oil starts moving to the conservator tank and thus the balloon structure inside compreses and with the help of breather air is sent out. Transformer in the opposite condition ,or say in extreme condition (lower temperature ),oil inside contracts and then air is taken inside to main the balloon like structure through silica gel breather .

Transformer in loaded condition-temperature increases inside main tank,oil inside starts heating and expands the excessive oil starts moving to the conservator tank and thus the balloon structure inside compreses and with the help of breather air is sent out. Transformer in the opposite condition ,or say in extreme condition (lower temperature ),oil inside contracts and then air is taken inside to main the balloon like structure through silica gel breather .

Answer / parag. Function of the cooling tubes is basically to maintain the working tempareture of the transformer. it's basically used to dissipate heat.there are 2 types of cooling

Different Transformer Cooling Methods For accelerating cooling different transformer cooling methods are used depending upon their size and ratings. We will discuss these one by one below, ONAN Cooling of Transformer This is the simplest transformer cooling system. The full form of ONAN is "Oil Natural Air Natural".

P.S. The power (P) of both generators and transformers is expressed in VA (volt-ampères) and is for generators the amount of power it produces, while for transformers it’s the amount of power it can transform. The power delivered to the transformer is almost the same als the power delivered by it.

P.S. The power (P) of both generators and transformers is expressed in VA (volt-ampères) and is for generators the amount of power it produces, while for transformers it’s the amount of power it can transform. The power delivered to the transformer is almost the same als the power delivered by it.

A generator transforms non-electric (mostly kinetic) energy to electric energy. It is mostly driven by a turbine (that is driven by water or steam), or by an engine on gas, etc. A transformer transforms electric energy to electric energy, most of the time changing voltage and current, when the electric energy provided is not suited for applications.

But when single line to ground fault occurs on any phase of the system, as shown in the figure, zero sequence component of the earth fault current flows in the earth and returns to the electrical power system by way of earth star point of the earthing transformer.

The rated voltage of an earthing or grounding transformer is the line to line voltage on which it is intended to be used. Current rating of this transformer is the maximum neutral current in Amperes that the transformer is designed to carry in fault condition for a specific time. Generally the time interval, for which transformer designed to ...

The induction voltage regulator is essentially a step-down transformer in which the output voltage may be varied from zero to a certain maximum value depending upon the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary windings.The primary windings are connected to the circuit to be regulated, and secondary is connected in series with the circuit.

The induction voltage regulator is essentially a step-down transformer in which the output voltage may be varied from zero to a certain maximum value depending upon the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary windings.The primary windings are connected to the circuit to be regulated, and secondary is connected in series with the circuit.

Transformer insulation is based on basic impulse insulation level together with voltage rating. Insulating media in up to 11KV transformer is mostly comprised of paper wrapped around the conductor in transformer coils, mineral oil and pressboard to insulate the coil from the ground.

In transformer, the eddy current loss is proportional to the square of the diameter of the core.larger the diameter, more the eddy current loss. Hence transformer core is laminated so that the net effective diameter of the transformer core reduces and thus eddy current loss can be minimized.
In transformer, the eddy current loss is proportional to the square of the diameter of the core.larger the diameter, more the eddy current loss. Hence transformer core is laminated so that the net effective diameter of the transformer core reduces and thus eddy current loss can be minimized.

A generator transforms non-electric (mostly kinetic) energy to electric energy. It is mostly driven by a turbine (that is driven by water or steam), or by an engine on gas, etc. A transformer transforms electric energy to electric energy, most of the time changing voltage and current, when the electric energy provided is not suited for applications.

Conservator Tank of a Transformer This is a cylindrical tank mounted on supporting structure on the roof the transformer main tank. The main function of conservator tank of transformer is to provide adequate space for expansion of oil inside the transformer.

The basic function of a Phase-Shifting Transformer is to change the effective phase displacement between the input voltage and the output voltage of a transmission line, thus controlling the amount of active power that can flow in the line.

Three phase transformer core has three sets of windings. Those sets of primary and secondary windings will be connected in either Δ or Y configurations to form a complete unit. The various combinations of ways that these windings can be connected together in will be the focus of this section.

P.S. The power (P) of both generators and transformers is expressed in VA (volt-ampères) and is for generators the amount of power it produces, while for transformers it’s the amount of power it can transform. The power delivered to the transformer is almost the same als the power delivered by it.

Unit auxiliary transformers (UAT) that connect the generator directly to the generator auxiliary load In such a station, the UAT will typically be subjected to the most severe operational stresses. Abnormal conditions have been found to result from several occurrences in the operation of the station.

A tap changer is a device fitted to power transformers for regulation of the output voltage to required levels. This is normally achieved by changing the ratios of the transformers on the system by altering the number of turns in one winding of the appropriate transformer/s.

In general, a toroidal inductor/transformer is more compact than other shaped cores because they are made of fewer materials and include a centering washer, nuts, and bolts resulting in up to a 50% lighter weight design.

Transformer oil or insulating oil is an oil that is stable at high temperatures and has excellent electrical insulating properties. It is used in oil-filled transformers, some types of high-voltage capacitors, fluorescent lamp ballasts, and some types of high-voltage switches and circuit breakers.

An autotransformer has a single winding with two end terminals, and one or more terminals at intermediate tap points, or it is a transformer in which the primary and secondary coils have part of, or all of their turns in common.

A winding is the name given each of the coils wound around the transformer's core. A basic transformer has two windings, termed the primary winding (connected to the supply) and the secondary winding (connected to the load).

In some high rating transformer, one winding in addition to its primary and secondary winding is used. This additional winding, apart from primary and secondary windings, is known as Tertiary winding of transformer. Because of this third winding, the transformer is called three winding transformer or 3 winding transformer.