Types of Virtualization

A virtualization administrator is an employee whose responsibilities include virtual environment set up and maintenance, in addition to traditional sysadmin duties. That virtual environment could consist of operating systems, network resources, servers, storage, desktops, applications and/or data.

Server virtualization makes each virtual server look and act like a physical server, multiplying the capacity of every single physical machine. The concept of server virtualization is widely applied in IT infrastructure as a way of minimizing costs by increasing the utilization of existing resources.
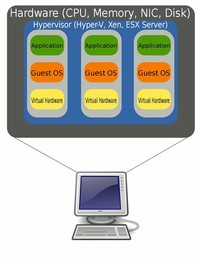
Hardware virtualization is the abstraction of computing resources from the software that uses those resources. Today, hardware virtualization is often called server virtualization or, simply, virtualization.
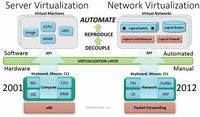
Network virtualization (NV) is defined by the ability to create logical, virtual networks that are decoupled from the underlying network hardware to ensure the network can better integrate with and support increasingly virtual environments.

In OS virtualization, the operating system is altered so that it operates like several different, individual systems. The virtualized environment accepts commands from different users running different applications on the same machine. The users and their requests are handled separately by the virtualized operating system.
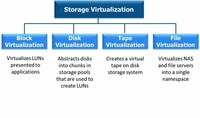
Storage virtualization is the pooling of physical storage from multiple network storage devices into what appears to be a single storage device that is managed from a central console.