Types of Distillation

Distillation of high-boiling and/or air sensitive materials. Distillation is used to separate compounds based on differences in boiling point. Vacuum distillation allows for this purification technique to be used on compounds with high boiling points, or those which are air-sensitive.
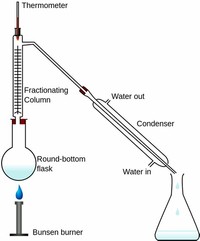
Fractional distillation is the process of taking a chemical mixture and using heat to separate out the various components in that mixture. When you think of this process, the first word that should come to mind is separation.

Short-path distillation is a distillation technique that involves the distillate travelling a short distance, often only a few centimeters, and is normally done at reduced pressure. A classic example would be a distillation involving the distillate travelling from one glass bulb to another, without the need for a condenser separating the two chambers.
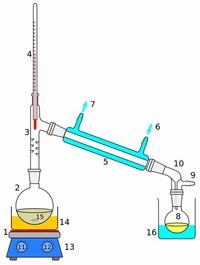
Simple distillation condenses the liquid once, so the boiling points of the two liquids must be far apart to make it efficient. The number of simple distillations in a fractional distillation apparatus depend on the length and efficiency of the fractionating column. The process is the same; the difference is mainly one of iteration.

Steam distillation is useful for the purification of organic compounds, although vacuum distillation is more common. When organics are distilled, the vapor is condensed. Because water and organics tend to be immiscible, the resulting liquid generally consists of two phases: water and the organic distillate.

Zone distillation Zone distillation is a distillation process in long container with partial melting of refined matter in moving liquid zone and condensation of vapor in the solid phase at condensate pulling in cold area.